More than 70% of men remain unaware of the true cause behind infertility, repeated in vitro fertilization (IVF) failures, and unsuccessful conception attempts. The distressing reality is that the underlying and often overlooked cause is DNA fragmentation—commonly referred to as sperm DNA damage.
This article discusses the primary causes of sperm DNA fragmentation, its diagnosis using advanced laboratory techniques, and evidence-based treatment strategies aimed at preventing infertility and other health issues associated with sperm DNA damage.
Causes of DNA Fragmentation in Sperm
DNA fragmentation (DNA damage) within sperm cells can result from a variety of intrinsic, environmental, and lifestyle-related factors. The most significant of these include:
1. Internal Factors (Related to the Male Body)
- Genital Tract Infections: Conditions such as prostatitis or epididymitis generate free radicals that damage sperm DNA.
- Varicocele: Enlarged scrotal veins raise testicular temperature and reduce oxygen supply, leading to oxidative stress and DNA injury.
- Advanced Age: Increasing paternal age correlates with a higher risk of sperm DNA breaks.
- Chronic Testicular Heat Exposure: Frequent sauna use, prolonged sitting, or wearing tight clothing contributes to DNA instability.
- Defective DNA Repair Mechanisms: Genetic or hormonal abnormalities may impair the sperm’s ability to correct DNA errors.

2. Environmental Factors
- Exposure to Radiation and Chemicals: Pesticides, heavy metals, paints, and industrial solvents are major contributors.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Both increase oxidative stress and reduce sperm quality.
- Air Pollution: Particularly oxidative compounds from vehicle exhausts and industrial emissions.
- Prolonged Use of Electronic Devices: Keeping laptops or mobile phones close to the pelvic area for extended periods increases heat and radiation exposure.
3. Lifestyle-Related Factors
- Poor Nutrition: Deficiency in antioxidants such as Vitamins C and E, zinc, and selenium accelerates DNA damage.
- Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Associated with systemic inflammation and hormonal imbalance.
- Chronic Stress and Sleep Deprivation: Disrupt hormonal regulation and elevate oxidative stress.
- Certain Medications or Therapies: Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and some hormonal or fertility treatments may induce DNA breaks.
Major Health Implications of Sperm DNA Fragmentation
DNA fragmentation can lead to several reproductive disorders, including:
- Male Infertility or Unexplained Subfertility: Damaged sperm are often unable to fertilize oocytes effectively.
- Recurrent Miscarriage: High DNA fragmentation in the male partner can cause repeated pregnancy loss in female partners.
- Poor Embryo Quality: Even with assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF or ICSI, sperm DNA damage significantly reduces fertilization and implantation success rates.
Diagnosis of Sperm DNA Fragmentation
The condition is diagnosed through a sperm DNA fragmentation test (DNA Fragmentation Assay), which evaluates the integrity and quality of sperm DNA by quantifying the percentage of spermatozoa carrying fragmented or damaged genetic material.
This percentage is expressed as the DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI).
A higher DFI indicates greater DNA instability and correlates strongly with reduced semen quality, lower natural conception rates, and decreased success in assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF or ICSI.


How Is the DNA Fragmentation Test Performed?
A semen sample is collected from the patient following standard semen analysis procedures.
At Al Safa Laboratory, the sample is processed using highly specialized assays, including:
- TUNEL assay (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling)
- SCSA (Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay)
- Comet assay
- Halosperm test
These advanced molecular techniques utilize fluorescence microscopy and computer-assisted analysis to detect and quantify DNA strand breaks in individual sperm cells.
Clinical Significance of the DNA Fragmentation Test
Helps explain unexplained infertility cases where standard semen parameters appear normal.
Identifies the underlying cause of recurrent miscarriage in couples with otherwise normal fertility assessments.
Guides clinicians in selecting the most suitable treatment approach, including the optimal assisted reproduction technique (natural conception vs. ICSI).
Enables evaluation of treatment effectiveness after varicocele repair or antioxidant therapy.
🔹 In short: The test provides essential diagnostic insight into male infertility by revealing DNA integrity — a factor not detectable through routine semen analysis.
Pre-Test Requirements and Preparation
To ensure accurate and reliable results, specific pre-test conditions must be followed:
- Abstinence period: Avoid ejaculation for 2–5 days prior to sample collection.
- Timely delivery: Submit the semen sample to the laboratory within 30–60 minutes after collection.
- Temperature control: Keep the sample at room temperature; do not expose it to heat or cold.
- Medication guidance: Follow medical advice regarding any ongoing medications or supplements.
- Health status: Postpone the test if the patient has had fever, infection, or any acute illness, as these can affect accuracy.
When Is the DNA Fragmentation Test Recommended?
Physicians recommend performing the sperm DNA fragmentation test under the following conditions:
- Unexplained infertility despite normal semen parameters.
- Repeated failure of IVF or ICSI procedures.
- Presence of varicocele or chronic genital tract inflammation.
- Long-term exposure to smoking, heat, or environmental pollutants.
- Recurrent miscarriage in the female partner.
Treatment of Sperm DNA Fragmentation
Understanding the therapeutic strategies for sperm DNA fragmentation is key to enhancing male fertility potential and improving outcomes of both natural conception and assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Treatment depends primarily on identifying and addressing the underlying cause and can be categorized as follows:
1. Management of Underlying Causes
Varicocele Repair (Microsurgical or Conventional):
Varicocele is one of the most significant contributors to DNA damage. Surgical correction reduces testicular heat and oxidative stress, resulting in substantial improvement in DNA integrity within 3–6 months post-surgery.
Treatment of Chronic Genital Tract Infections:
Management involves appropriate antibiotic therapy guided by semen culture results, combined with antioxidant supplementation to minimize reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Hormonal Imbalances:
In cases of hypogonadism or testosterone deficiency, hormone replacement or regulation should be undertaken under the supervision of an andrology specialist.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
Cessation of Smoking and Alcohol:
Both tobacco and alcohol significantly increase oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation. Discontinuation leads to measurable improvement in semen parameters within 2–3 months.
Avoidance of Heat Exposure:
Limiting the use of saunas, hot tubs, and tight clothing helps maintain optimal testicular temperature.
Stress Management and Adequate Sleep:
Chronic psychological stress and sleep deprivation elevate cortisol levels and impair spermatogenesis.
Healthy Diet and Exercise:
A diet rich in antioxidants and regular physical activity improve overall hormonal balance and sperm DNA stability.
3. Antioxidant and Nutritional Therapy
Antioxidants play a vital role in neutralizing free radicals and promoting DNA repair mechanisms in sperm cells.
Commonly recommended supplements include:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Zinc
- Selenium
- L-Carnitine
- Coenzyme Q10
- Folic Acid
Note: Supplementation should always be medically supervised and maintained for at least 3 months to achieve measurable improvement.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
If sperm DNA fragmentation remains elevated despite medical and lifestyle interventions, advanced ART techniques may be employed to improve fertilization outcomes:
- IMSI (Intracytoplasmic Morphologically Selected Sperm Injection): Allows microscopic selection of sperm with normal morphology and intact DNA.
- PICSI (Physiological ICSI): Utilizes hyaluronic acid binding to select mature, biochemically competent sperm.
- MACS (Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting): Separates apoptotic (DNA-damaged) sperm from healthy ones using magnetic labeling.
- These advanced selection methods significantly improve embryo quality, increase implantation rates, and reduce miscarriage risk.
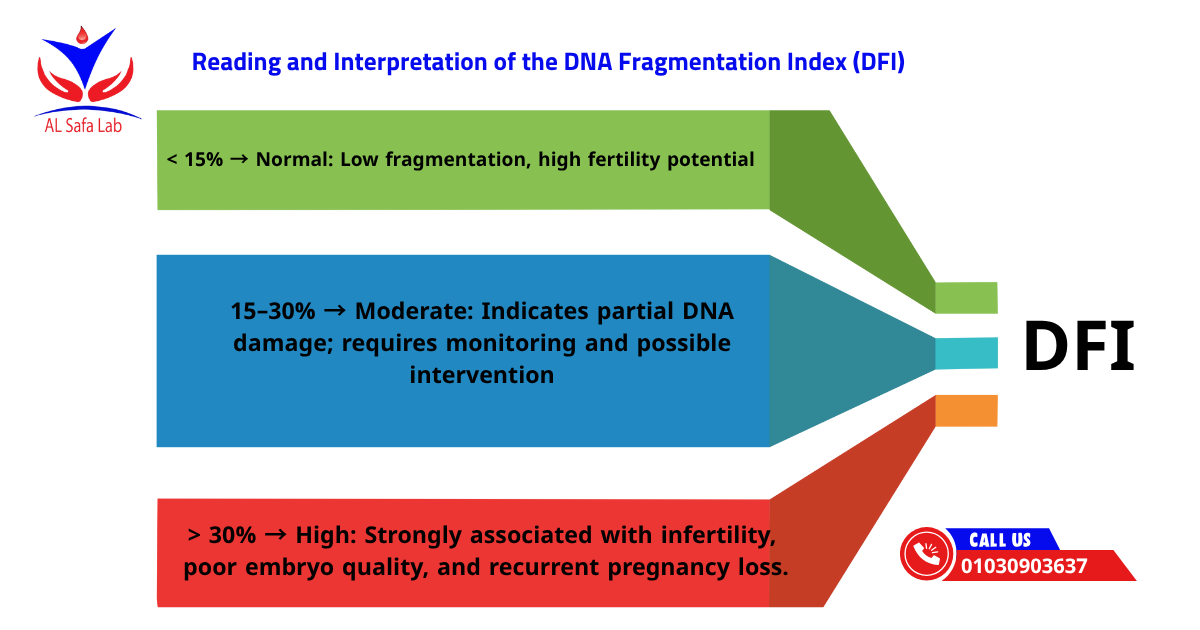
Reading and Interpretation of the DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI)
Laboratory experts interpret DFI results according to the following thresholds:
- DFI < 15% → Normal: Low fragmentation, high fertility potential.
- DFI 15–30% → Moderate: Indicates partial DNA damage; requires monitoring and possible intervention.
- DFI > 30% → High: Strongly associated with infertility, poor embryo quality, and recurrent pregnancy loss.

Why Choose Al Safa Laboratory for DNA Fragmentation Testing?
Al Safa Laboratory is recognized among the most advanced medical laboratories in Egypt for its high-precision reproductive testing and male fertility diagnostics.
Key advantages include:
- Use of state-of-the-art computerized imaging and molecular diagnostic systems to assess DNA fragmentation accurately.
- Expert clinical interpretation to guide personalized treatment strategies.
- Comprehensive fertility assessment, including varicocele evaluation, oxidative stress profiling, and semen antioxidant capacity testing.
- Fast, safe, and minimally invasive sample handling procedures ensuring reliable results.

🔹 In conclusion:
The DNA fragmentation test is a crucial diagnostic tool that uncovers the hidden causes of male infertility, guiding clinicians toward targeted therapies and improved reproductive outcomes.
References:
